Metabolic engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans for pinene
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
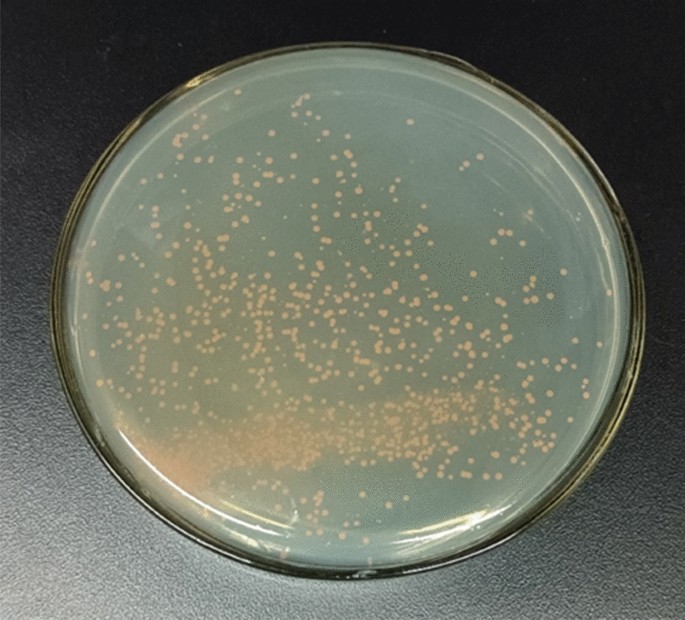
Background The objective of this work was to engineer Deinococcus radiodurans R1 as a microbial cell factory for the production of pinene, a monoterpene molecule prominently used for the production of fragrances, pharmaceutical products, and jet engine biofuels. Our objective was to produce pinene from glycerol, an abundant by-product of various industries. Results To enable pinene production in D. radiodurans, we expressed the pinene synthase from Abies grandis, the geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) synthase from Escherichia coli, and overexpressed the native 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase. Further, we disrupted the deinoxanthin pathway competing for the substrate GPP by either inactivating the gene dr0862, encoding phytoene synthase, or substituting the native GPP synthase with that of E. coli. These manipulations resulted in a D. radiodurans strain capable of producing 3.2 ± 0.2 mg/L pinene in a minimal medium supplemented with glycerol, with a yield of 0.13 ± 0.04 mg/g glycerol in shake flask cultures. Additionally, our results indicated a higher tolerance of D. radiodurans towards pinene as compared to E. coli. Conclusions In this study, we successfully engineered the extremophile bacterium D. radiodurans to produce pinene. This is the first study demonstrating the use of D. radiodurans as a cell factory for the production of terpenoid molecules. Besides, its high resistance to pinene makes D. radiodurans a suitable host for further engineering efforts to increase pinene titer as well as a candidate for the production of the other terpenoid molecules.

04 Terpenoides Compilation, PDF, Adenosine Diphosphate

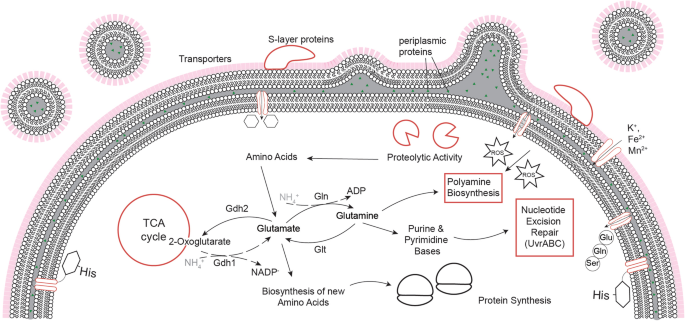
The schematic of the terpene synthetic pathway and the functional
PDF) Metabolic engineering of Deinococcus radiodurans for pinene production from glycerol
The Toughest Organisms on Earth: Evolution of Radio-Resistance Is More Complicated Than Previously Thought

Week 1 Discussion Micro.docx - Microbiology is both a basic and an applied science. It is not a single subject! It has many areas of specialization

Research Progress of Plant Prenyltransferases

Chalmers Research: Ivan Mijakovic

Microbial synthesis of pinene.
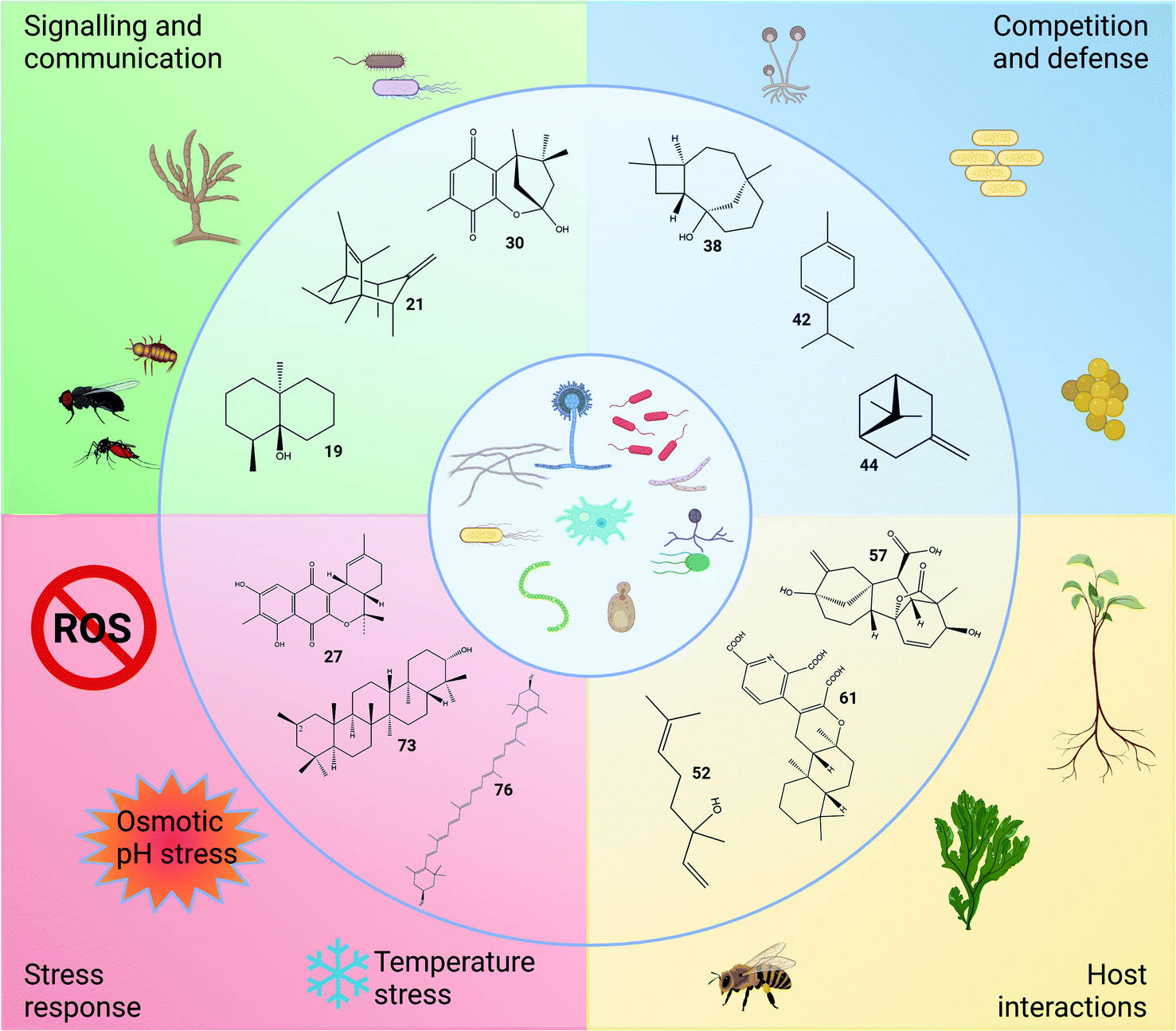
Biosynthesis, evolution and ecology of microbial terpenoids - Natural Product Reports (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1NP00047K

Functionalized Nanomaterial Assembling and Biosynthesis Using the Extremophile Deinococcus radiodurans for Multifunctional Applications - Li - 2019 - Small - Wiley Online Library
Life, Free Full-Text
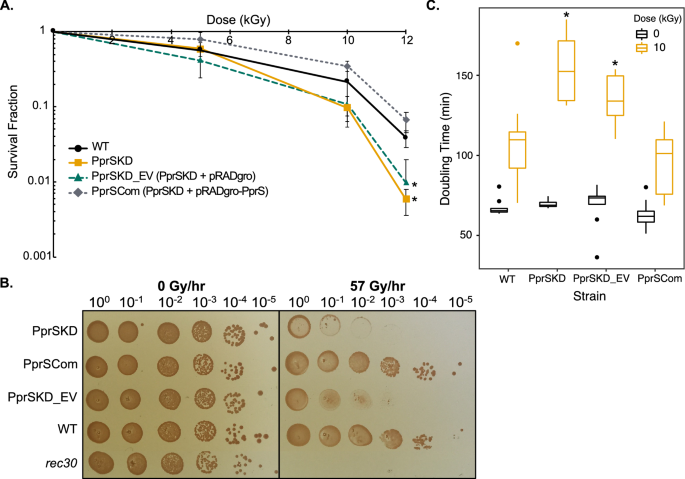
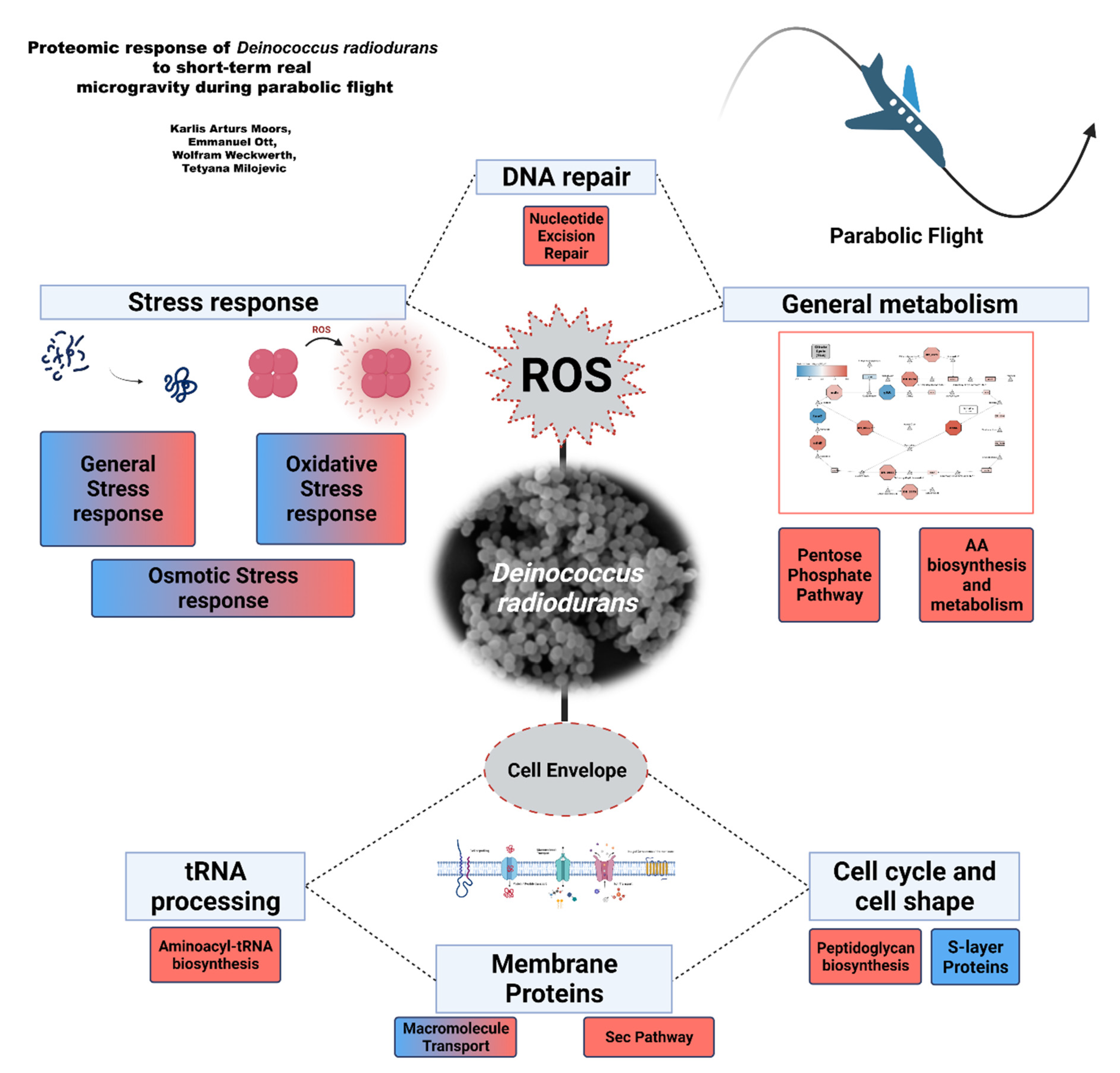
A small RNA regulates pprM, a modulator of pleiotropic proteins promoting DNA repair, in Deinococcus radiodurans under ionizing radiation

A Novel Small RNA, DsrO, in Deinococcus radiodurans Promotes Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase (msrA) Expression for Oxidative Stress Adaptation

WO2012135591A2 - Microbial isoprenoid production using a heterologous dxp pathway - Google Patents

Analysis of codon usage patterns in Morus notabilis based on genome and transcriptome data
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)